PCR062: Screening patterns and identification of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obese children in Canadian primary care
Rebecca Theal; Rachael Morkem, MSc; John Queenan, PhD, BA, MSc; David Barber, MD, BSc
Abstract
Context. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common cause of chronic liver disease in children. There is no epidemiological data on rates of pediatric NAFLD in Canada. Primary care physicians (PCPs) are often the first contact healthcare professionals to manage potential pediatric patients with NAFLD.
Objective: Evaluate patterns of screening and identification of pediatric NAFLD in Canadian primary care using administrative health care database.
Study Design: Cross-sectional observational study.
Dataset: The Canadian Primary Care Sentinel Surveillance Network (CPCSSN), a repository of clinical electronic medical record data drawn from primary care practices across Canada. Population Studied: Children aged 9-18 years old between July 1, 2018 and December 31, 2019.
Outcome Measures: The proportion of children eligible for screening (BMI≥95th percentile) as per NASPGHAN guidelines using ALT levels. Logistic Regression was used to evaluate the predictors for screening. Suspected NAFLD was defined as elevated ALT (>22 U/L for girls and > 26 U/L for boys) in the absence of viral hepatitis, metabolic conditions, alcohol use, hepatotoxic medications.
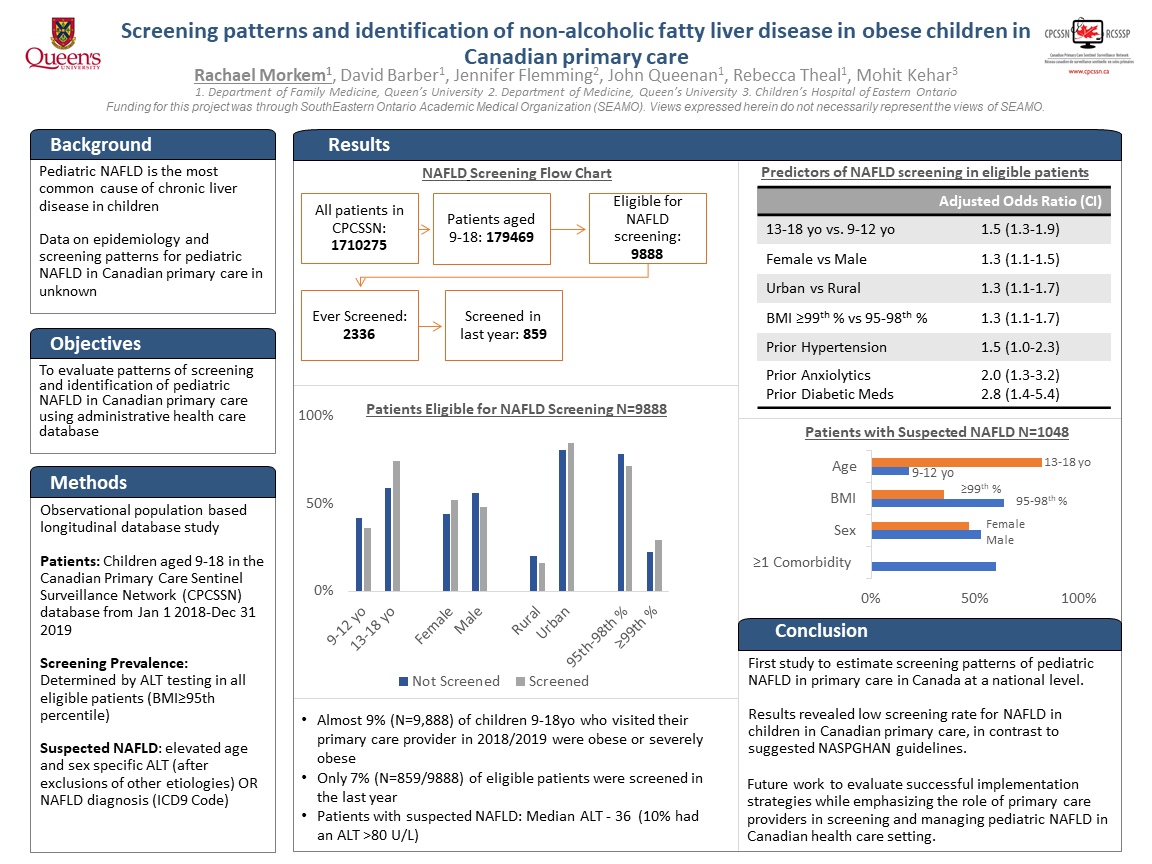
Results: The study sample consisted of 66,872 children, of which 15.8% (n=10,539) had a BMI≥95th percentile and only 10.1% (n=1,067/10539) were screened in the last year using ALT. Children were more likely to get screened if they were a) older (13-18 year vs 9-12 year, OR=1.63, 95% CI 1.38-1.93); b) living in an urban setting (OR=1.34, 95% CI 1.0-1.63); and c) had a higher BMI (≥99th percentile vs 95th-98th, OR=1.34, 95% CI 1.14, 1.56). We identified 855 cases of suspected NAFLD, most children (78.5%) were older (13-18 years), male (55.0%), and lived in an urban setting (71.5%). A significant proportion (40.4%) had a BMI in the 99th percentile and 60.3% had at least one comorbidity, and 35.9% were prescribed a psychotropic, antidiabetic or antihypertensive medications. Only 19.9% were referred to a specialist (pediatrician, gastroenterologist).
Conclusions: This is the first study to estimate the screening patterns of pediatric NAFLD in primary care in Canada at a national level. The study revealed low screening rates in primary care, these results will help facilitate prioritization of care and future work that could evaluate successful implementation strategies while emphasizing the role of PCPs in screening and managing pediatric NAFLD in Canadian health care setting.
Objective: Evaluate patterns of screening and identification of pediatric NAFLD in Canadian primary care using administrative health care database.
Study Design: Cross-sectional observational study.
Dataset: The Canadian Primary Care Sentinel Surveillance Network (CPCSSN), a repository of clinical electronic medical record data drawn from primary care practices across Canada. Population Studied: Children aged 9-18 years old between July 1, 2018 and December 31, 2019.
Outcome Measures: The proportion of children eligible for screening (BMI≥95th percentile) as per NASPGHAN guidelines using ALT levels. Logistic Regression was used to evaluate the predictors for screening. Suspected NAFLD was defined as elevated ALT (>22 U/L for girls and > 26 U/L for boys) in the absence of viral hepatitis, metabolic conditions, alcohol use, hepatotoxic medications.
Results: The study sample consisted of 66,872 children, of which 15.8% (n=10,539) had a BMI≥95th percentile and only 10.1% (n=1,067/10539) were screened in the last year using ALT. Children were more likely to get screened if they were a) older (13-18 year vs 9-12 year, OR=1.63, 95% CI 1.38-1.93); b) living in an urban setting (OR=1.34, 95% CI 1.0-1.63); and c) had a higher BMI (≥99th percentile vs 95th-98th, OR=1.34, 95% CI 1.14, 1.56). We identified 855 cases of suspected NAFLD, most children (78.5%) were older (13-18 years), male (55.0%), and lived in an urban setting (71.5%). A significant proportion (40.4%) had a BMI in the 99th percentile and 60.3% had at least one comorbidity, and 35.9% were prescribed a psychotropic, antidiabetic or antihypertensive medications. Only 19.9% were referred to a specialist (pediatrician, gastroenterologist).
Conclusions: This is the first study to estimate the screening patterns of pediatric NAFLD in primary care in Canada at a national level. The study revealed low screening rates in primary care, these results will help facilitate prioritization of care and future work that could evaluate successful implementation strategies while emphasizing the role of PCPs in screening and managing pediatric NAFLD in Canadian health care setting.
Jack Westfall
jwestfall@aafp.org 11/20/2021i keep learning new things at NAPCRG. Thanks for this study and presentation.